由于Scala本身属于JVM下的语言,因此它能够较好地与Java项目融合在一起。在Scala中调用Java库,基本上与在Java中调用Java库的方式是相同的(反过来则未必,必将Java没有Scala中独有的语法糖)。因此,在Scala中可以非常方便地调用Spring Cloud,使其支持Spring Cloud提供的微服务基础设施,例如Eureka、Feign以及Spring Boot等。
不过仍然有几点需要注意,这些方面包括:
- Maven依赖
- Spring的语法
- Json的序列化
Maven依赖
在Scala项目中,如果仍然使用Maven管理依赖,则它与在Java项目中添加Spring Boot依赖几乎完全相同,不同在于项目要支持Scala,需要添加对Scala语言库的依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.scala-lang</groupId>
<artifactId>scala-library</artifactId>
<version>2.11.11</version>
</dependency>
|
要支持用ScalaTest编写单元测试,则还需要添加:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.scalatest</groupId>
<artifactId>scalatest_2.11</artifactId>
<version>3.0.4</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
|
同时,添加对编译Scala代码的插件依赖:
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.codehaus.mojo</groupId>
<artifactId>build-helper-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>1.10</version>
<executions>
<execution>
<id>add-source</id>
<phase>generate-sources</phase>
<goals>
<goal>add-source</goal>
</goals>
<configuration>
<sources>
<source>src/main/scala</source>
</sources>
</configuration>
</execution>
<execution>
<id>add-test-source</id>
<phase>generate-test-sources</phase>
<goals>
<goal>add-test-source</goal>
</goals>
<configuration>
<sources>
<source>src/test/scala</source>
</sources>
</configuration>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>net.alchim31.maven</groupId>
<artifactId>scala-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.2.2</version>
<executions>
<execution>
<goals>
<goal>compile</goal>
<goal>testCompile</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
|
Spring的语法
Scala语言中照样可以使用Java的Annotation,因此scala项目的Application,可以这样实现:
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableDiscoveryClient
class SqlEngineApplication
object SqlEngineApplication extends App {
SpringApplication.run(classOf[SqlEngineApplication], args: _*)
}
|
注意,Spring Cloud以及Spring Boot提供的annotation是运用在类上面的,而Scala可以运用的Application则可以直接定义为与类同名的object。
而对于Spring Boot的Controller,在语法上有少许差异,即在值中要使用Scala的Array类型,例如:
@RestController
@RequestMapping(Array("/"))
class SqlStatementController extends SqlGenerator {
@RequestMapping(value = Array("/sql"), method = Array(GET))
def getSql:String = ???
@RequestMapping(value = Array("/sql"), method = Array(POST))
def generateSql(@RequestBody request: GenerateSqlRequest): String = ???
}
|
Json的序列化
添加依赖
Spring Boot使用Jackson作为Json的序列化支持,若要在Scala项目也要使用Jackson,则需要添加jackson对scala的支持模块:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.module</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-module-scala_2.11</artifactId>
<version>2.8.7</version>
</dependency>
|
添加WebConfig
同时还需要添加WebConfig,告诉Spring Boot选择Scala Module对对象进行映射:
@Configuration
class WebConfig extends WebMvcConfigurerAdapter {
override def configureMessageConverters(converters: java.util.List[HttpMessageConverter[_]]): Unit =
converters.add(jackson2HttpMessageConverter())
@Bean
def jackson2HttpMessageConverter(): MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter =
new MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter(objectMapper())
@Bean
def objectMapper(): ObjectMapper =
new ObjectMapper() {
setVisibility(PropertyAccessor.FIELD, Visibility.ANY)
registerModule(DefaultScalaModule)
}
}
|
对多态的支持
客户端发过来的Request中,包含了一棵表达式树。这棵树的节点分为两种类型:
- Condition Group
- Condition
Condition Group作为根节点,可以递归嵌套Condition Group和Condition,如下图所示:
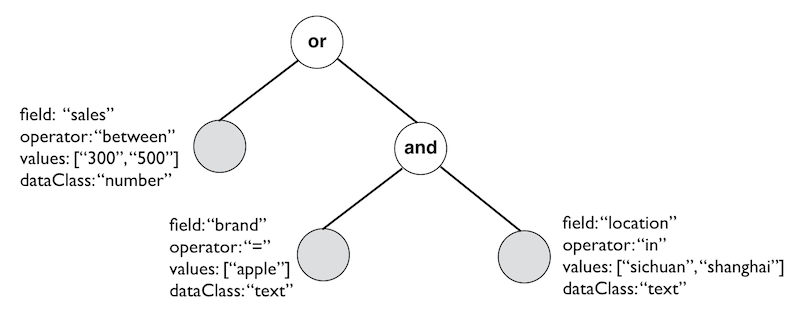
在Scala中的定义如下所示:
case class GenerateSqlRequest(sqlTemplateName: String, criteria: Option[ConditionGroup] = None, groupBy: List[GroupByField] = Nil)
abstract class ConditionExpression {
def evaluate: String
}
case class ConditionGroup(logicOperator: String, conditions: List[ConditionExpression]) extends ConditionExpression
case class Condition(fieldName: String, operator: String, values: List[String], dataType: String) extends ConditionExpression
|
GenerateSqlRequest中包含的criteria属性的类型就是前面提及的表达式树,它对应的Json结构需要支持Json类型的多态,即前面代码所示的ConditionExpression抽象类型,子类ConditionGroup与Condition拥有不同的属性定义。要支持这种Json的多态,则必须在抽象类型ConditionExpression上添加如下annotation:
@JsonTypeInfo(
use = JsonTypeInfo.Id.NAME,
include = JsonTypeInfo.As.PROPERTY,
property = "type")
@JsonSubTypes(Array(
new Type(value = classOf[Condition], name = "condition"),
new Type(value = classOf[ConditionGroup], name = "group")
))
abstract class ConditionExpression {
def evaluate: String
}
|
即使ConditionGroup与Condition子类没有定义type属性,在对应的Json结构中也需要添加type,并给出符合上述代码定义的值:
{
"sqlTemplateName": "name1",
"criteria": {
"type": "group",
"logicOperator": "and",
"conditions": [
{
"type": "condition",
"fieldName": "sales",
"operator": "between",
"values": ["3", "100"],
"dataType": "Integer"
},
{
"type": "group",
"logicOperator": "or",
"conditions": [
{
"type": "condition",
"fieldName": "brand",
"operator": "=",
"values": ["apple"],
"dataType": "String"
},
{
"type": "condition",
"fieldName": "location",
"operator": "in",
"values": ["Sichuan", "Shanghai"],
"dataType": "String"
}
]
}
]
},
"groupBy": [
{
"fieldName": "location"
},
{
"fieldName": "brand"
}
]
}
|
注意,这种对多态的支持不仅仅是针对Scala,同样支持Java:
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonIgnoreProperties;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonSubTypes;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonTypeInfo;
@JsonIgnoreProperties(ignoreUnknown = true)
@JsonTypeInfo(use = JsonTypeInfo.Id.NAME, include = JsonTypeInfo.As.PROPERTY)
@JsonSubTypes({
@JsonSubTypes.Type(value = Condition.class, name = "condition"),
@JsonSubTypes.Type(value = ConditionGroup.class, name = "group") }
)
public abstract class ConditionExpression {}
|
一旦在Scala项目中使用了Spring Boot以及Spring Cloud,在编译打包后,使用方式和普通Java项目结合Spring Boot与Spring Cloud是完全一样的,毕竟scala编译后生成的就是一个不同的Jar包。
